August 1, 2017
Clinical studies to understand how dietary supplements alter drug metabolism
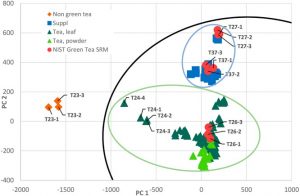
The Center of Excellence for Drug Interaction Research (NaPDI) provides leadership on how best to study potential adverse interactions between plant-based natural products (herbal medicines) and conventional medications. The center is composed of a uniquely experienced and multidisciplinary team, led by Dr. Mary Paine at Washington University. Other key investigators include Dr. Nicholas Oberlies and Dr. Nadja Cech (University of North Carolina Greensboro), Dr. Craig Hopp (National Institutes of Health) and Dr. Richard Boyce (University of Pittsburgh). The team has identified a priority list of four dietary supplement natural products that may influence how drugs are metabolized and, in turn, alter the efficacy and safety of conventional medications. Throughout the duration of the 5 year study, each of these will be studied in the laboratory and in clinical trials. The first clinical trial, with green tea, is currently under way. One of the challenges with research on botanical natural products is handling their inherent variability and complexity. Using green tea as an example, the analytical core (Cech, Oberlies, and coworkers) has developed novel methodologies to profile commercially available botanical products, to compare their chemical profiles, and to identify potential active components. Under the auspices of NaPDI, the group has recently published several publications on this topic.

Could any of these green tea products cause toxic interactions with prescription drugs?
NaPDI scientists seek to find out.
Kellogg, J. J.; Wallace, E. D.; Graf, T. N.; Oberlies, N. H.; Cech, N. B. Conventional and accelerated-solvent extractions of gree tea (Camellia sinsnsis) for metabolomics-based chemometrics. 2017, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 145, 604-610.
PMID: 28787673 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.07.027

Kellogg, J. J.; Graf, T. N.; Paine, M. F.; McCune, J. S.; Kvalheim, O. M.; Oberlies, N. H.; Cech, N. B. Comparison of Metabolomics approaches for evaluating the variability of complex botanical preparations: Green tea (Camellia sinensis) as a case study, 2017, J. Nat. Prod., 80, 1457-1466.
PMID: 28453261 PMCID: PMC5469520 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b01156